Bitcoin launch in 2009 was a true technological revolution – it was the very first practical implementation of blockchain technology.
Nowadays it is used in virtually all spheres of our life: from the financial sector and e-commerce to shipping and information security blockchain gradually turns into a habitual part of all systems handling data.
Why Are People Crazy About Blockchain?
What does blockchain technology have to offer that makes the entire world obsessed with it? From the tech community to government agencies – it seems like everybody wants to integrate blockchain into their data structures. And often they are willing to go to great lengths in order to do so.
Well, the main advantage of the blockchain is absolute data security – data stored in a blockchain is tamper-proof and every data piece can be traced back to its origin via a chain of previous transactions involving said data. The benefits of such a system are obvious, aren’t they?
Blockchain Technology Is Not Perfect
However, it doesn’t mean that blockchain is the perfect technology for data storage and processing. There is a fair share of issues.
Thus, it was inevitable that people started to modify blockchain to alleviate these issues and to develop completely different alternative solutions. And one of if not the most promising of such alternatives is Tangle.
So let’s take a look at how these technologies differ from one another.
What Is Blockchain?
Despite the fact that blockchain is mostly known for supporting cryptocurrencies (the most famous are Bitcoin and Ethereum, but there are hundreds and hundreds more) it is not its sole application.
In essence, a blockchain is a database comprised of cryptographically connected data blocks. Data in every block is encrypted and every subsequent block contains a hash of the previous one.
It is not possible to restore a block from its hash, however, if a block is changed – its hash also changes. Therefore, it is impossible to retroactively change, add or delete data in a block – it will no longer fit in a chain of cryptographically connected data blocks.
Naturally, if a blockchain is fully centralized, it only means that no one, except the owner, can change data in it. But the owner, who has complete control over the database, can still edit it.
To prevent this. blockchain architecture facilitate decentralization. A good example of a decentralized blockchain data structure is the Bitcoin network.
Decentralization Is Key
Typical blockchain (such as the Bitcoin network) isn’t stored on any “central server:, instead, it is stored on thousands upon thousands of data nodes all across the world. Every node has its own full-fledged copy of the blockchain.
And there is a very simple mechanism that determines, which copy is correct – a blockchain version that over 50% of nodes (also called miners or validators) consider “correct” is the “proper” version of the blockchain.
Thus, if any malicious actor wants to do anything to the data stored in the blockchain, they have to have the support of a majority of the miners.
And miners are not interested in compromising the blockchain, since it incentivizes their honest work in support of a blockchain network.
What Do Miners Do in a Blockchain?
Miners (or validators. depending on a specific blockchain network) independently verify transactions in a blockchain, assemble them into blocks and add blocks to the chain.
Whoever assembles a block first (usually – a solution to a mathematical problem) – receives a reward in cryptocurrency. Other miners check the validity of a proof of consensus, attached to the block, and if it is valid – the block is added to the chain.
As you can see – blockchain technology is extremely robust, reliable and well-protected against malicious actors (at least if there are enough miners\validators active). Thus, it is not surprising that it has found application in many spheres, besides powering cryptocurrencies.
DApps – The Future of Blockchain
In recent years the most prominent and demanded feature of blockchain is support of decentralized applications (DApps) deployment. DApps are similar to other applications that we use on our phones and computers and are just as diverse in their purpose.
However, a DApps is not controlled by anybody – once an application is deployed in a blockchain network, it works autonomously.
DApps are powered by smart contracts – self-executing open-source algorithms that can’t be tampered with and can be verified by anyone.
Another huge advantage of DApps is that they grant customers full custody over their personal data.
Blockchain Issues

While blockchain technology is extremely secure, it is “clunky”. Scalability problem is the inherent issue of blockchain technology: the more people use a blockchain, the slower and more congested it becomes.
And there is no simple solution to this problem since in a decentralized network you can’t just update hardware by an executive decision.
All blockchain developers work constantly on the scalability issue, but there is no denying the fact that decentralized blockchain networks are always slower than centralized “traditional” data structures.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
So let’s quickly summarize the pros and cons of blockchain technology.
Pros
- Great reliability;
- High level of security
- Decentralization
- The scalability problem gradually becomes less pressing
Cons
- Scalability issues are not going anywhere
- Relatively slow transaction confirmation
- High transaction fees in most blockchains
- Energy efficiency issues
While blockchain technology is undoubtedly one of the most important innovations of the last couple of decades, its issues spurred the development of alternative solutions. One such solution is the Tangle network.
What Is Tangle?
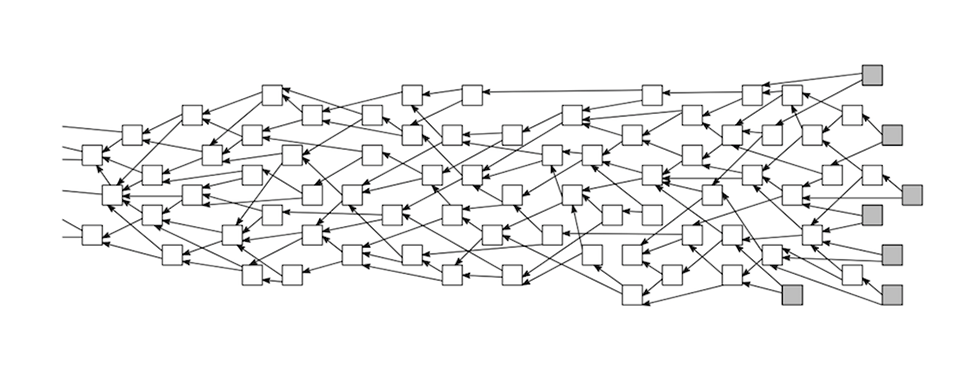
Tangle is a decentralized network that tries to facilitate transactions in a trustless environment, just like blockchain.
Tangle is also “somewhat decentralized”. While there is no single decision-making entity, there is a “coordinator” – a centralized “guardian” of the network.
So in terms of decentralization Tangle is somewhere in between centralized systems and “traditional” blockchains.
However, despite similar objectives, the core of the Tangle network is fundamentally different from the blockchain. It is based on a directed acyclic graph (DAG) – which is also a distributed ledger like the blockchain, but does not require miners to process transactions and is much more scalable due to flexible adjustments of data unit sizes.
Finally, much more relaxed transaction confirmation rules (it is enough to validate two previous transactions in order to add a new one to the network) make Tangle much faster and more energy efficient.
Unlike blockchain, the Tangle network is very well suited to micro-transactions. In fact, micro-transactions processing is its main design goal, since it is specifically tailored to the Internet of Things (IoT).
Internet of Things – The Ultimate Goal of Tangle
IoT is a concept of a global network of connected devices that can interact with one another through a multitude of unique identifiers to enable them to execute their functions without human intervention. It may sound very sci-fi and very complicated, but it is in fact rather simple.
Imagine a coffee machine that makes coffee 5 minutes before you wake up and restocks your coffee and milk supplies automatically, by placing orders on a delivery platform – that is the most basic level of IoT.
However, it is obvious that a huge number of transactions must be processed very quickly for such a system to be viable. And that’s what Tangle developers strive to achieve. But there are problems with Tangle as well.
Tangle Problems
Tangle offers a very different set of compromises compared to blockchain. First of all, it is less secure – despite the use of a directed acyclic graph, more relaxed confirmation rules mean that transactions are verified faster, but not as meticulously.
Moreover, a centralized “coordinator node” presents an additional vulnerability of the data structure that can, in theory, be exploited. Moreover, a directed acyclic graph, while looking great in theory, is not proven in comparison to blockchain technology.
Finally, Tangle is lagging behind in terms of acknowledgment and adoption. It does not support DApps, it is not well-trusted by the IT community. Basically, the only real implementation of Tangle is IOTA
What Is IOTA?

IOTA virtual coin is designed to facilitate the Internet of Things (it is rather obvious, isn’t it?). IOTA can handle micro-transactions in huge volume, which is ideal for the IoT concept. However, since the Internet of Things hasn’t gained a lot of traction yet, the coin is not widely used.
Pros and Cons of Tangle
So, a quick summary of Tangle’s main advantages and disadvantages
Pros
- No transaction fees
- Fast transaction processing
- Great scalability
Cons
- A lower level of security
- No DApps support
- Centralization
- Limited adoption
Blockchain vs. Tangle: What to Choose?
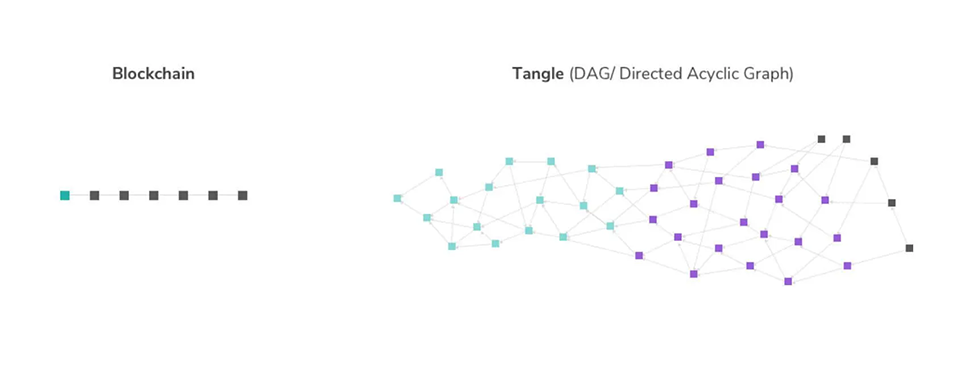
These technologies have a lot of similarities, especially when it comes to general concepts. However, they have very significant differences in technical implementation.
Blockchain offers better security thanks to its extremely meticulous block confirmation process and full decentralization.
On the other hand, Tangle’s is much faster, far more energy efficient, and does not require users to pay transaction fees for transaction processing. In other words, these technologies, while somewhat similar, are tailored to different purposes.
If you need to handle very sensitive data – blockchain is by far a better solution due to its inherent reliability.
However, if you need to process a huge number of transactions on a regular basis and the security of a single transaction is less of a pressing issue – Tangle suits your needs better.