Il Concetto di Programmazione Criptata
In breve, la programmazione criptata è lo sviluppo software utilizzando tecnologie blockchain, nonché la loro combinazione con framework e linguaggi più familiari come React e C++.
La criptovaluta e lo sviluppo blockchain stanno diventando sempre più richiesti. Si tratta di un lavoro con salari elevati, un numero infinito di posizioni aperte e un potenziale illimitato per il futuro. È il grande fondamento per il futuro che spinge queste tecnologie molto avanti.
Il punto è che le criptovalute e la blockchain formeranno la base dell’economia del futuro, in cui sistemi finanziari decentralizzati avranno il sopravvento. E la tecnologia blockchain stessa si è rivelata abbastanza universale da essere utile non solo in ambito strettamente finanziario (investimenti, aste, relazioni commerciali, ecc.), ma anche in altri settori dell’attività umana.
Scegliendo la programmazione criptata, creerai programmi come gli altri sviluppatori, ma sotto il cofano dei tuoi progetti ci sarà sempre il codice direttamente correlato alle tecnologie più avanzate esistenti.
Cos’è un Sviluppatore di Criptovalute?
Un sviluppatore di criptovalute è una persona che non è solo vicina ai computer e sa come creare una pagina o un codice, ma è un programmatore ben versato nelle tecnologie della finanza decentralizzata. Nel migliore dei casi, ha esperienza nel lavorare con il componente backend dei programmi, e nel peggiore dei casi, almeno comprende come scrivere il codice di un programma in linea di principio.
Un tale sviluppatore è impegnato nella creazione del codice backend per applicazioni decentralizzate, chiamate Dapp. Di solito, queste applicazioni esistono sulla rete Ethereum e non sono altro che smart contract.
Ethereum è un intero ambiente blockchain che consente a chiunque di eseguire programmi in un ambiente affidabile supportato da smart contract.
Ethereum è un intero ambiente blockchain che consente a chiunque di eseguire programmi in un ambiente affidabile supportato da smart contract.
A differenza di Bitcoin, la piattaforma Ethereum consente di interagire non solo con le criptovalute, ma anche con altri dati. I programmi corrispondenti vengono eseguiti in un ambiente chiamato EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). Questo permette di convertire il codice scritto dalle persone in un insieme di caratteri digeribili dalla blockchain e supporta gli smart contract creati per svolgere determinate attività all’interno della blockchain. Utilizza anche la sua valuta, chiamata Ether.
A differenza di Bitcoin, la piattaforma Ethereum consente di interagire non solo con le criptovalute, ma anche con altri dati. I programmi corrispondenti vengono eseguiti in un ambiente chiamato EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). Questo permette di convertire il codice scritto dalle persone in un insieme di caratteri digeribili dalla blockchain e supporta gli smart contract creati per svolgere determinate attività all’interno della blockchain. Utilizza anche la sua valuta, chiamata Ether.
Ethereum is a whole blockchain environment that allows everyone to run programs in a trusted environment supported by smart contracts.
Unlike Bitcoin, the Ethereum platform allows you to interact not only with cryptocurrencies but with other data too.
The corresponding programs are run in an environment called EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). It allows you to convert code written by people into a set of characters that is digestible for the blockchain and supports smart contracts created to perform certain tasks inside the blockchain. It also uses its own currency, called Ether.

This is the largest system of its kind and at the same time the most popular one. In most cases, employers are looking for crypto programmers to create software that will be implemented in the Ethereum project interface.
Smart Contracts
This is code that runs in an EVM environment and is capable of processing data transmitted to it, Ether or any logic. For smart contracts, functions are written that allow manipulating the information transmitted to them. You can share data with other smart contracts or, based on the information received, broadcast between smart contract users.
A smart contract allows you to exclude a third party from any transaction. The program code will be responsible for justice: open, incorruptible and working correctly.
Crypto programmers are engaged in smart contacts creation, allowing the inhabitants of the blockchain network to make transactions related to Ether.
What Languages and Libraries Are Used in Crypto Programming?
To create smart contracts and other components of the cryptocurrency network, both traditional general-purpose languages and new ones created specifically for working with Ethereum or its analogues are used.
The four most popular ones include:
- Solidity. It is a leader in the field. The first language worth learning is to start creating DApps and smart contracts. The language is based on JavaScript and C++ syntax. It has strict typing and a fairly low entry threshold for beginners. We’ll talk about the Solidity Ethereum development language later in this article.
- Java. A powerful platform that has proven itself in dozens of areas of development, including the creation of software for mobile operating systems. It is in demand in the blockchain environment due to strict adherence to the principles of OOP and the abundance of libraries required when working with cryptocurrencies.
- Vyper. A safe and functional programming language with syntax borrowed from Python. It is focused on working with EVM and creating smart contracts.
- Python. Python itself couldn’t get past this top either. One of the most universal and ubiquitous languages has also found its place in the blockchain real world.
How to Start a Career in Crypto Programming?
The threshold for entering the profession is impossible. Due to the high demand, the requirements are not particularly strict, but mere enthusiasm is not enough. It is necessary to acquire basic knowledge and delve into the study of blockchain programming languages.
What Do I Need to Learn, and What Do I Need to Know?
To begin with, it is worth reading about the blockchain in general. We need to understand how the whole system works in general terms. Familiarity with the technical features of the implementation is optional, at least in the early stages.
After that, you need to decide on the language. For beginners, Solidity is recommended, as it is easier to understand. The next stage should be either an in-depth study of the documentation with constant independent practice or a visit to the appropriate courses.
In terms of equipment, you don’t need anything. It is enough to open a web IDE called Remix and write your first smart contract according to the instructions on the official Solidity website.
Which Environment in Remix IDE Can Be Used to Connect a Private Test Network?
You can access the Remix IDE in various ways: via the Internet, via a web browser such as Chrome, from a local copy, or from Mist (the Ethereum Dapp browser).
Using the In-Browser Remix IDE
You can access the Remix IDE from your web browser without any special installation. Visit https://remix.ethereum.org, and you will be presented with a complete IDE with a code editor and various panels for compiling, running and debugging your smart contracts. You will have an example contract with a default newsletter that you can play with.
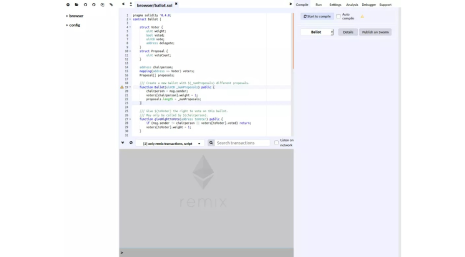
Remix IDE
After Solidity, you will have to learn the frameworks used: Truffle to simplify the creation of smart contracts, Ganache to test software in a virtual blockchain network, Web3.js for connecting the backend component of your brainchild with the front part (it can be React or Vue).

On the online courses, you will be educated in all aspects at once. Many active Solidity developers got into the profession straight after the courses. The average training time takes less than six months.
Perspectives and Future
Crypto programming is a new stage of the developer’s profession, which is constantly gaining popularity. If you are interested in promising and monetary work, you should pay attention to blockchain development.

A Practical Guide to Ethereum Development. Solidity Smart Contract Programming.
If you are creating an Ethereum-based DApp or an ERC20 token, you need to learn the Solidity language. Although blockchains are language-independent and many of the existing languages are used by blockchain engineers, there are some tasks that cannot be conveniently implemented by existing ones. It has opened up demand for new, crypto-specific options. One of these languages is Solidity.
Regardless of whether you are an experienced developer or just starting out in cryptography, it would be a good idea to start studying Solidity because smart contracts have become an important part of the blockchain ecosystem. In addition to the active implementation of dApps, they are actively integrated into infrastructure-level blockchains and even into bitcoins through providers such as RSK. Knowing how to create smart contracts, you can track the way blockchain programmers work and will be able to have better solutions.
Solidity Documentation
Smart Contracts Basics
As part of development, the smart contract consists of three sections: balance, storage and codes. The balance represents how much Ethereum a smart contract has. The storage contains data such as strings and arrays that are specific to each and every application. The code section contains raw machine code that is compiled from what we write in Solidity.
Unlike user accounts, smart contract accounts are not external to the respective networks. In other words, you can use your wallet on various networks like Kovan and Ropsten, but you can’t do it with a smart contract. Smart contracts are internal.
Each smart contract has a source that is stored on the author’s device and instances that are stored in the blockchain. To create an instance (account) of a smart contract, we need to deploy it on the network. It is very similar to the relationship between classes and instances in traditional object-oriented programming (OOP) and the languages representing it (JS, Ruby). To give you a more visual representation, let’s create a Bike class and add an instance of it.
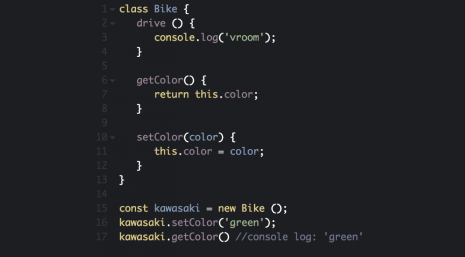
Bike class & instance
We will write a contract definition, which will then be run through a compiler that will create two files: a bytecode and a binary application interface (ABI). The bytecode is what will actually be passed to the EVM, and the ABI is the layer between the bytecode and the regular JavaScript code that allows you to create a user interface (UI).
Choosing an IDE and Solidity Version
Before we get started, we need a proper Integrated Development Environment (IDE). In other words, we need a convenient terminal with the necessary tools to write our code. For the purposes of this guide, we will choose Remix, an IDE created by the Ethereum Foundation that allows you to write, test, debug, run smart contracts and much more. You can use it either directly in the browser or download it locally if you want.
After running the Remix, you will see a code editor in the center, a file manager on the left, and a compiler on the right.
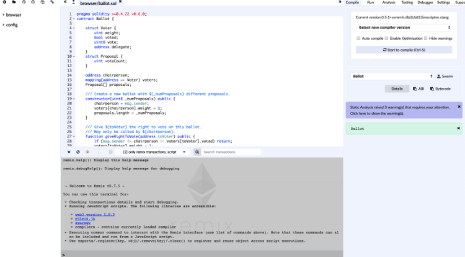
Initial Remix window
There will be some pre-written code — we won’t need it. To create the first unique smart contract, let’s click on the plus icon in the upper left corner of the terminal and give it a name.
Creating a new project in Remix
Because we have an empty document. sol, we have to specify the Solidity version that the compiler will run. At the time of writing this guide, the latest version was 0.5.7. If you are not sure which version to use, you can specify a range of versions.

2 types of specifying the Solidity version
Let’s give our smart contract a name, followed by parentheses.
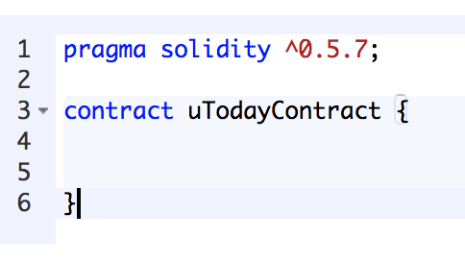
Naming the contract
Writing Your First Smart Contract
Once we have the canvas ready, it’s time to define the main building blocks — variables. Although experienced software developers will have no problems understanding this concept, we will briefly introduce it to beginners. Variables are placeholders for portions of information that are subsequently referenced by the program that runs them.
Let’s create a pair of variables: a string (a sequence of characters) and an integer (a number). In the case of Ethereum, variables are stored in the blockchain along with the rest of the contracts and, therefore, can be accessed and updated from anywhere. Another key characteristic of Solidity variables is that you can make them private by writing “private” next to the variables. Finally, for integers, Solidity has two types: signed (can be positive and negative) and unsigned (can only be positive). To specify an unsigned variable, we should just put ‘u’ in front of it.
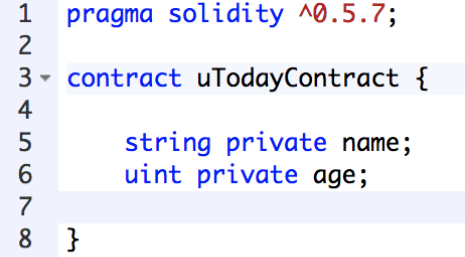
A private string and an integer
When we have a name variable, we need to write the methods of setting and receiving. This is similar to the JS function. Remember that Solidity has static typing, so we have to define the types of variables. Now any value we put in ‘setName’ will define the string ‘name’. To get it, we will use getName and specify which variable we expect to see. Now it’s time to do the same for the age variable. The method is constructed similarly to getName.
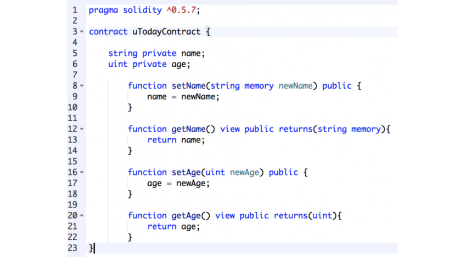
Name/age setters and getters
Let’s check out our little piece of code. Go to the “Run” tab of the compiler and click “Deploy” under the name of your contract. At the very bottom of the compiler, you will see the section “Deployed Contracts”, where our methods are available. To pass the name to the value “Newname”, we need to make sure that our string is written in JSON. Otherwise, “getName” will not return anything. For “setAge”, just specify your age without quotes. As you can see, we can now set and receive the name and age variables through our smart contract.
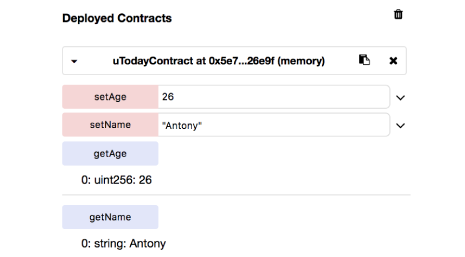
Compiler, name and age
What Are Wei and Gas?
One of the most remarkable features of smart contracts is that in order to deploy them on the Ethereum network, you will need to initiate a transaction that costs a certain amount of money, which is paid in Ether. It is extremely important to understand how fees are used in the system, as they will be deducted every time you interact with EVM.
What Is Wei?
Let’s assume that while reading our lesson, you have used Bitcoin at least once. You probably made a small transaction that cost less than 1 BTC. In this case, you used Satoshi, something like cents on the dollar. Wei is similar to Satoshi — it is the smallest part of 1 Ether. If we think about it from a programming perspective, this is the lowest unsigned integer on the network. Interacting with the network, you most often encounter Gwei, which belongs to Gigawee and is equal to 1 billion Wei.
What Is Gas?
Gas is an integral part of the smart contract execution mechanism. It has two values for each transaction: the Gas consumed and its price. It is worth noting that the user initiating the transaction determines these values himself. However, if the set Gas value is not enough to perform a certain operation, then Gas will be consumed, but the transaction will not be executed. Moreover, if the gas price is set too low for the network at a given time, the transaction will not be processed by the nodes, which will ultimately make it unsuccessful. There are several services to check the optimal values for your transactions, one of which is ethgasstation.info. To better understand Gas and why it costs some money, let’s start coding some of them ourselves.
Go back to the Remix window and create a new file. In our example, we will call it “Gas” and create a contract with the same name. Keep in mind that the more data we need to store on the blockchain, the more Gas we will need. At the same time, for the purposes of this lesson, we will create a cheap contract; The more you add to it, the higher the fee will be.
There is a function that returns an integer that is the sum of two inputs. To make it as easy as possible, we will indicate that our contract will not store anything in the blockchain, and for this, we will add “pure” next to the function.
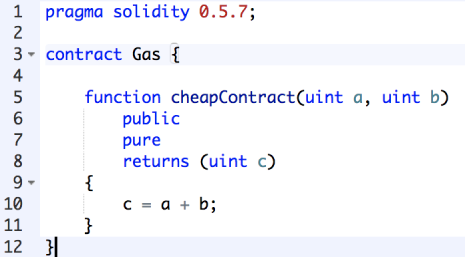
Cheap contract
Now you can expand it in the compiler and enter any two numbers to get the integer “c”. To check the price of our transaction, we have to look at the terminal located under the code section. There is a transaction cost and an execution cost. The first refers to how much data the transaction has. The second refers to how much EVM energy was required for the transaction.
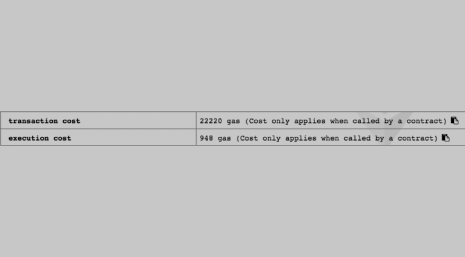
Indeed, more complex and data-intensive smart contracts will incur higher transaction fees on the network due to the increased computational and storage demands. As developers work on real-world applications and blockchain solutions, they need to carefully consider the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their contracts to ensure they are feasible for use in a production environment. Understanding gas costs and optimizing contracts is an essential aspect of Ethereum and blockchain development.
Creazione e Distribuzione del Tuo Token ERC20 Personale. Emissione del Token e Creazione di un ICO.
Diciamocelo, la maggior parte degli sviluppatori blockchain che stanno iniziando tendono a puntare in alto e creare le proprie blockchain e token. Anche se si tratta di un argomento estremamente complesso che ha attirato alcuni dei migliori sviluppatori software provenienti da altri settori, la creazione di un token ERC20 di base non è un compito difficile.

ERC20 Standard
La funzione totalSupply ci permette di vedere quanti token abbiamo in totale. La funzione balanceOf viene utilizzata per ottenere il numero di token in determinati indirizzi. La funzione transfer consente agli utenti di effettuare transazioni tra di loro. Le funzioni “transferFrom”, “allow” e “approve” consentono agli utenti di permettere ad altri utenti di avviare transazioni per loro conto. Gli eventi sono strumenti di registrazione per il registro generale.
Oltre all’interfaccia stessa, avremo bisogno di un file .sol separato per il nostro nuovo token. Qui importiamo l’interfaccia ERC20 e specifichiamo il simbolo, il nome e il numero decimale del nostro token.
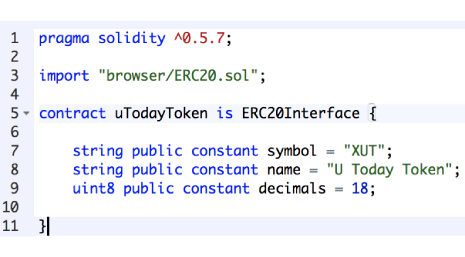
uToday token
Prima di compilarlo, dobbiamo specificare i vincoli.
- Iniziamo con una frase generale: questa è una variabile intera costante, che renderemo privata. Il totale dei nostri token sarà di 1 milione. Scriveremo anche una funzione per restituire questo valore.
- In secondo luogo, abbiamo bisogno di conservare i nostri token da qualche parte. Per fare ciò, dovremo specificare un mapping che restituirà il saldo per un qualsiasi indirizzo specificato.
- In terzo luogo, dovrebbe esserci una funzione per il trasferimento di token, che avrà fondamentalmente l’indirizzo del destinatario e il numero di token trasferiti.
- Questa funzione dovrebbe anche essere in grado di verificare se il mittente ha abbastanza token nel suo saldo, che può essere implementato utilizzando una semplice dichiarazione if/then. Inoltre, stabiliremo delle condizioni per ‘_value’ in modo che gli utenti non possano inviare transazioni con “0” token, poiché ciò porterebbe all’ingorgo della rete con varie informazioni inutili.
- In quarto luogo, abbiamo bisogno di creare un mapping per il resto delle funzioni, che è un mapping intero.
Successivamente, specificheremo diversi controlli nelle funzioni “approve” e “allow” e stabiliremo le condizioni per ‘transferFrom’. - Infine, non tutti i token saranno disponibili sul mercato. Alcuni dei token sono di solito riservati per team, fondazioni, consulenti e altri scopi. Pertanto, è importante chiarire quanti token circoleranno nel sistema. Quando creiamo i token, l’offerta negoziabile è uguale al nostro saldo.

uToday token constraints
Il codice è pronto, quindi procediamo a verificarlo. Vai alla scheda “Esegui” del compilatore e espandi il contratto dei nostri token. Vedrai che abbiamo i dati del token, nonché l’offerta generale, i saldi e le sovrattasse. Congratulazioni, hai creato il tuo primo token.
Affinché il nostro token funzioni davvero sulla rete, dobbiamo distribuire un contratto intelligente (nota che questo è diverso dalla distribuzione per scopi di test in Remix). Per questo tutorial, utilizzeremo Remix e Metamask, ma ci sono altre modalità per farlo. Metamask è un programma portafoglio Ethereum semplice ma efficace con un’interfaccia utente gradevole che si integra come estensione in alcuni dei browser più popolari. Nel nostro caso, utilizzeremo Opera. Per prima cosa, vai su metamask.io e scarica l’estensione. Una volta fatto ciò, vedrai l’icona della volpe nell’angolo superiore destro del tuo browser.
Fai clic sull’icona e segui le istruzioni suggerite per creare un portafoglio. Non dimenticare di salvare la frase segreta! Una volta che hai un portafoglio, fai clic sull’icona di Metamask e cambia la rete su “Ropsten” perché non vogliamo interferire con la rete principale di Ethereum.
L’ultimo passo è creare un po’ di Ether (purtroppo, non sarai in grado di usarlo per acquisti reali, ma è necessario per i test). Vai su faucet.metamask.io e richiedi 1 Ether.
Ora hai tutto pronto. Torna alla finestra di Remix e cambia l’ambiente in “Injected Web3” nel compilatore. Dai anche un’occhiata alla scheda degli account: il tuo indirizzo deve corrispondere all’indirizzo che hai creato in Metamask. Seleziona il contratto intelligente che desideri distribuire, che è il contratto dei tuoi token, ma non l’interfaccia ERC20, e fai clic sul pulsante appropriato. Una finestra di Metamask apparirà con la transazione, i suoi dettagli e le opzioni per interagire con essa. Invia una transazione, e il nostro token prenderà vita.
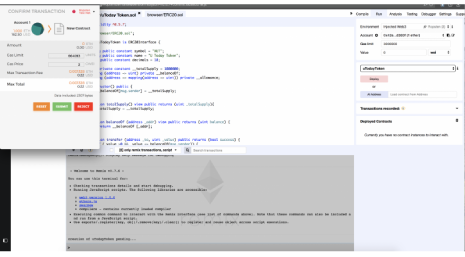
Ora puoi sperimentare tutte le funzionalità di cui abbiamo parlato in precedenza. Diamo un’occhiata al nostro contratto da un altro punto di vista per assicurarci che funzioni correttamente. Come qualsiasi altra blockchain, Ethereum dispone di diversi esploratori di blocchi che servono principalmente a monitorare ciò che accade sulla rete. Nel nostro caso, utilizzeremo etherscan, anche se ci sono diverse altre ottime alternative. Tieni presente che se accedi semplicemente a etherscan, vedrai la Main Network. Poiché dobbiamo vedere la rete Ropsten, dovrai inserire “ropsten” prima dell’indirizzo del sito. Trova il tuo indirizzo e vedrai due transazioni: una per l’Ether gratuito che hai ricevuto e l’altra per la distribuzione del contratto.
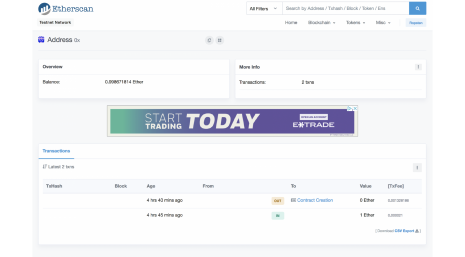
Per trovare l’indirizzo del tuo contratto, fai clic su TxHash e vai al campo “To”. Qui puoi verificare le transazioni, il codice e gli eventi del tuo contratto intelligente. In questo momento, dobbiamo verificare e pubblicare il nostro contratto. Vai alla sezione “Code” e fai clic sul link “Verify and Publish” ‘Verify and Publish’. Qui dovrai specificare nuovamente il nome del tuo token, la versione del compilatore (nel nostro caso, l’ultima versione di Solidity che abbiamo utilizzato era la 0.5.7, quindi dovremo aderire alla corrispondente versione del compilatore). Ora devi copiare il codice del contratto intelligente dei token insieme al codice dell’interfaccia ERC20 dalla finestra di Remix a etherscan e fare clic su “Confirm and Publish” ‘Verify and Publish’ in fondo alla schermata.
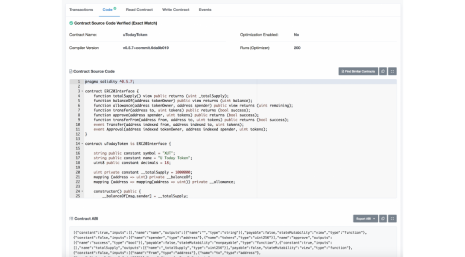
Smart contract verification
Se desideri intraprendere una carriera da sviluppatore nell’industria delle criptovalute, è importante comprendere che, nonostante la sua relativa semplicità nella sua essenza, la blockchain offre una flessibilità e funzionalità incredibili. A partire dal 2017, le blockchain hanno subito un notevole sviluppo, e i loro casi d’uso sono andati oltre le sole transazioni finanziarie. Con l’avvento di Ethereum, è emerso uno strato completamente nuovo di reti che ospita varie applicazioni dApp e soluzioni basate su blockchain. Lo strumento di questa evoluzione è stato un contratto intelligente, e se desideri espandere la tua esperienza, renderla più preziosa e orientata al futuro, è necessario capire come funziona.
Sebbene tu possa codificare contratti intelligenti utilizzando altri linguaggi, Solidity è comunque meglio adatto a questi scopi. Inoltre, se desideri diventare uno sviluppatore Ethereum o creare token ICO/ERC20 per il tuo progetto, questa è sicuramente la tua scelta. Se hai un po’ di esperienza con C++ o JavaScript, la codifica in Solidity dovrebbe risultarti relativamente facile. Tuttavia, dovrai comprendere alcune delle differenze tra i modelli di avvio del software client-server e decentralizzato. Grazie alla Ethereum Foundation e ad alcune organizzazioni di terze parti, gli sviluppatori dispongono di un set di strumenti comodi, come Remix ed Etherscan, per la codifica e la distribuzione di contratti intelligenti.
Speriamo che il nostro tutorial ti abbia aiutato a comprendere la maggior parte dei concetti di Solidity per iniziare un entusiasmante percorso di apprendimento della tecnologia blockchain. Ricorda che puoi sempre fare riferimento alla documentazione più recente di Solidity.



